CS641 Class 20 Handout: Intro to Verilog
Note: hw6 has new last problem re Verilog
HDLs: Hardware Description Language: Verilog
In serious use. With
today’s complexity of circuits, logic diagrams are almost useless.
Verilog is one of
two contenders, other is VHDL.
Verilog uses C
syntax, so best for us.
Important feature:
can build up little blocks into bigger blocks.
With this, we can “build”
little CPUs. Today: just combinational, plus R-S FF
Why not just use C?
or Java?
We could write a
function for a combinatorial circuit, but in C, we need to call it to get the
result, whereas in a circuit, it is calculated continuously.
Verilog has a “continuous
assignment” capability: set up a little machine that continuously reads from
inputs, expresses outputs.
Of course this is
implemented in software via event handling. But the abstraction is there for us
to use.
Also, work directly
with time, unlike in C/Java—make this happen, then that happen,...
Intro to Verilog: look at handout
Circuit Modules needed for parts of CPUs
Last time: register files
See picture on pg. 304, Fig. 4.2: several Mux’s. Inputs on one side, control signals coming in
at top or bottom.
Also in Fig. C.3.6, pg C-19
Data Multiplexor (here 2-to-1, n-bit-wide)
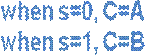
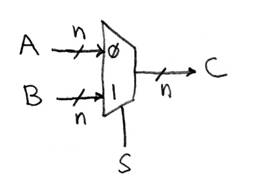
N instances of 1-bit-wide mux
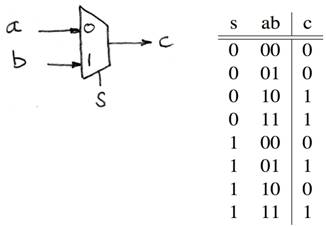
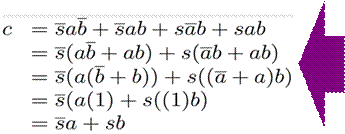
How do we build a 1-bit-wide mux?
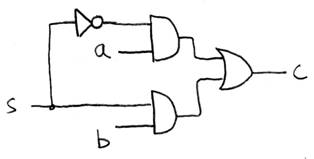
Look at diagrams on
pg. C-19.
Flip thru Chap 4,
see many MUX’s, all with 2 n-bit inputs, one n-bit output, one bit control
Is possible to have
more than 2 inputs, and more bits of control
Modules for CPUs, continued
Arithmetic and Logic Unit
°
Most processors contain a special logic block called
“Arithmetic and Logic Unit” (ALU)
°
We’ll show you an easy one that does ADD, SUB, bitwise
AND, bitwise OR
°

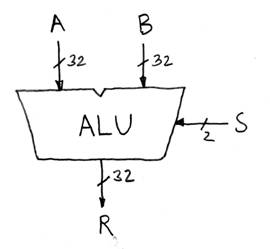
°
Our simple ALU
°
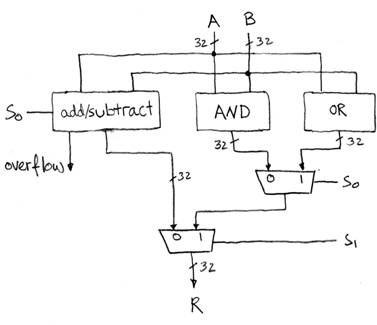
°
Adder/Subtracter Design -- how?
°
Truth-table, then determine canonical form, then
minimize and implement as we’ve seen before
°
Or, look at breaking the problem down into smaller
pieces that we can cascade or hierarchically layer
°
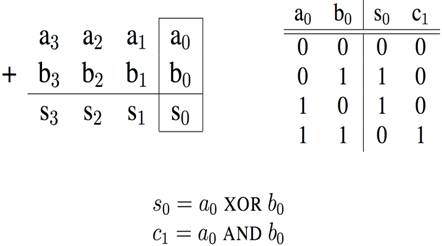
°
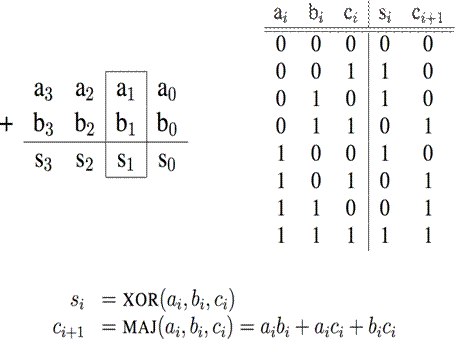
°
Adder/Subtracter – One-bit adder, for ith bit:
°
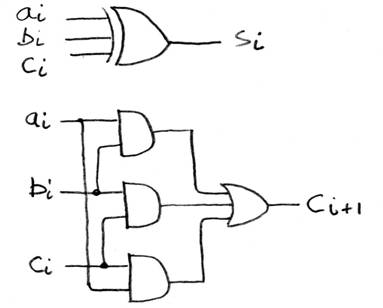
Next time: put together N 1-bit adders to make 1 N-bit adder