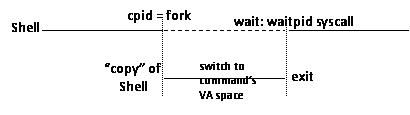Operating
System-Class 5-Feb. 9th
C: int
long int = long (same C type)
C99: long long = new type
C doesn’t fix the size in bytes of the numeric types, just requires that
sizeof(long long) >= sizeof(long) >= sizeof(int)
-
long long: 64 bits on most current system(that support C99)
-
long: 32 bits on (almost) all 32 bit platforms
-
int: 32 bits on almost all current platforms, including 64 bit platforms
64 bit Linux(sf06) has: sizeof(longlong) = 8
sizeof(long) = 8
sizeof(int) = 4
sizeof(void *) = 4 on 32-bit platform / 8 on 64-bit platform
DLL: can be loaded anywhere in address space
- the actual location isn’t known until runtime
o actual location of DLL: saved in memory variable.
o Then to call a function in the DLL, the actual address is loaded and the code does “jump %g1”(jump to loaded address)
UNIX (including
Linux) syscalls
- read, write, open, close
- exit
- int fork(): creates a process which is a clone of this process
o return 0 for the child (childpid for parent)
- exec*
o create a new virtual address space for given executable file
o redoes the current VA space
eg. Shell forks a new process, then use exec* syscall to run the command program in the new process.
- sounds wasteful, but memory management can avoid the memory copy
|
|
All syscalls: see Section 2 of man pages(syscall manual)
syscalls show all OS capability for a program, vary from UNIX to Windows.
- using syscalls directly in app program means no portability
-
![]() what to do?
standard C library – Section 3 of man
pages
what to do?
standard C library – Section 3 of man
pages
system to run a command, eg. system(“date”) <-- run in its own process
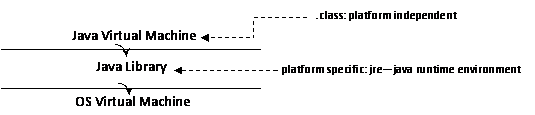 Java itself has a virtual machine!
Java itself has a virtual machine!
XINU syscall:
- int write
- int read
- int putc
- int getc
- int create(caddr, ssize, prio, name, nargs, args, …)
o caddr: start address
o ssize: stack size(create near-empty stacks, just the args)
o prio: priority
o nargs, args: args to pass to new process
o somewhat like Windows CreateProcess
- kill(pid)
o pid: can be own pid
o UNIX: use exit to kill self