Research
Welcome to CHiLL@UMB! We develop cutting-edge data management solutions for modern storage and memory devices and next-generation storage engines. Our current research focuses on ML-driven optimization of LSM-tree compactions, efficient operation of ZNS SSDs and CXL-enabled disaggregated database systems that can adapt to rapidly evolving hardware and workload demands. We are also exploring RL-inspired approaches to solve classical and emerging data management problems such as indexing and query optimization, with the goal of making data systems more autonomous and performance-stable in real deployments. In addition, we work on hardware/software co-design approaches using FPGA to support on-the-fly near-data transformation that supports efficient HTAP workloads. A key theme of our work is hardware-aware data management. We proposed the Parametric I/O Model that captures SSD read/write asymmetry and access concurrency, and used it to build device-aware systems including a database buffer pool manager, a graph manager, and an RL-based hierarchical storage manager that considers both workload and device properties.
Members
Tarikul Islam Papon (PI & Lab Director)
Shadman Saqib Eusuf (PhD Student)
Farhan S. Chowdhury (Graduate Researcher)
Aroma Hoque (Graduate Researcher)
Anindya Hoque (Graduate Researcher)
Saffat Zabin (Graduate Researcher)
Current & Past Projects
RL-Based LSM Compactions

We propose to tune LSM parameters via reinforcement learning based on workload properties.
UniZNS: Optimizing Any LSM Compactions for ZNS SSDs
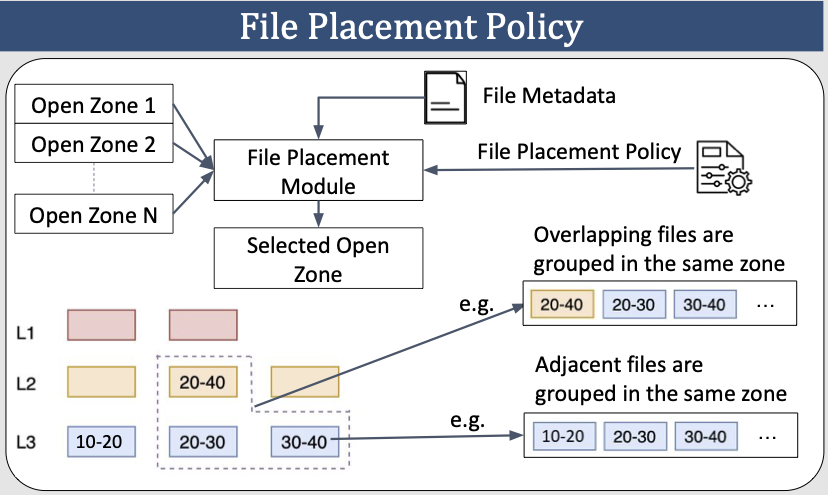
We introduce UniZNS, a platform that integrates any file placement, garbage collection, and zone allocation policies to identify the best combinations across different LSM compaction policies and workloads.
ReStore: RL-Based Page Migration in Tiered Storage

We propose a reinforcement learning-based page migration policy for a multi-tiered storage architecture that considers both workload and device (SSD) properties.
Learn moreCAVE Graph Manager

We develop a concurrency-aware graph manager CAVE that exploits full SSD parallelism and implement five popular graph traversal algorithms.
Learn moreACE Bufferpool Manager
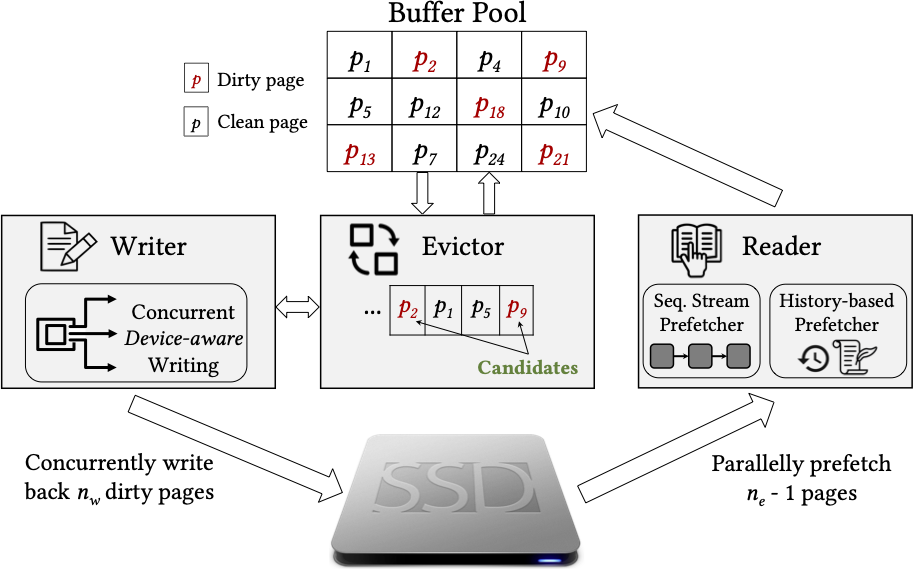
We propose an SSD-aware bufferpool manager ACE, that writes multiple dirty pages concurrently to amortize the asymmetric write cost.
Learn moreRelational Memory
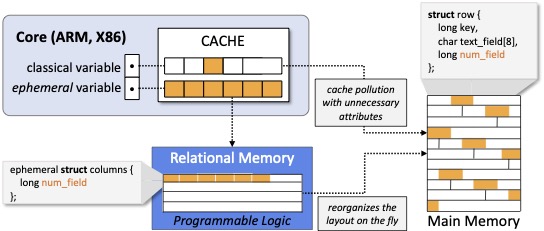
We introduce a new type of near-memory computation to transform between row-wise data to column-wise data on the fly via an FPGA-based custom hardware. This reduces cache pollution while ensuring optimal data layout for any query.
Learn moreThe New Parametric I/O Model
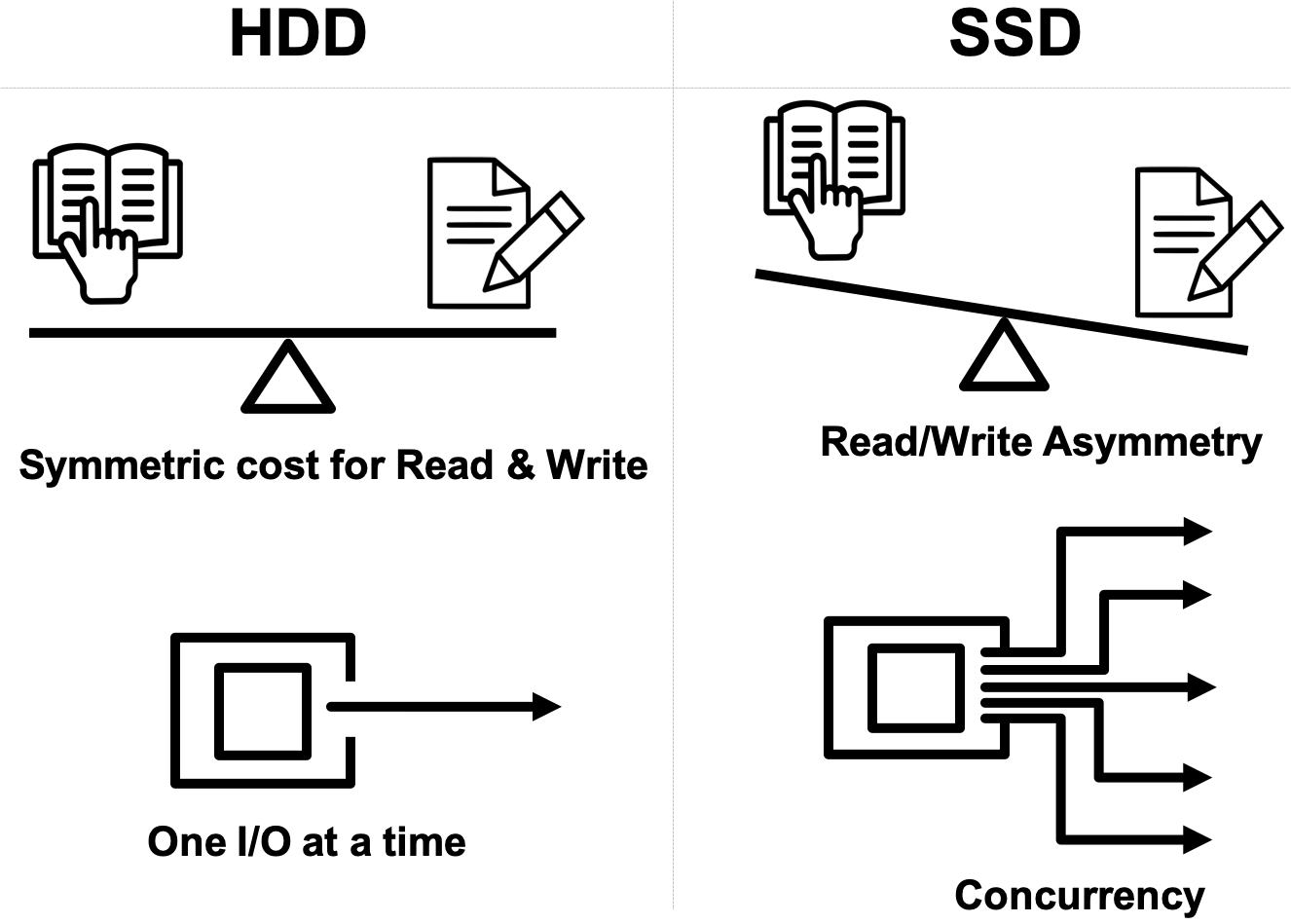
We propose a simple yet expressive I/O model that considers asymmetry and concurrency of contemporary storage devices.
Learn moreLethe: A Tunable Delete-Aware LSM Engine
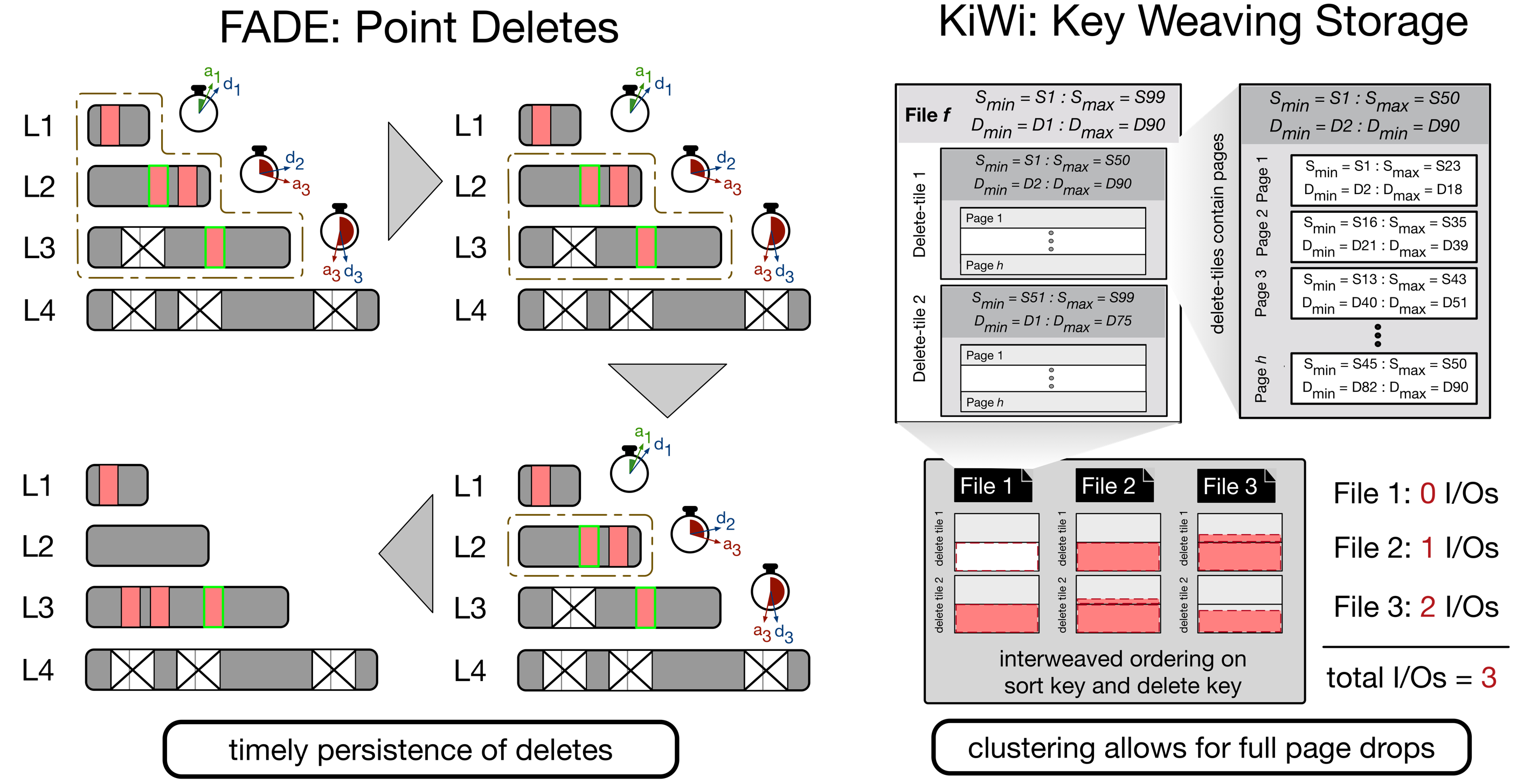
Lethe provides persistence guarantees for delete operations within bounded time and enables efficient secondary range deletes in LSM-based storage engines.
Learn more